Tell : 0086 135 1058 5626 E-mail : info@nasn.cn
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-09 Origin: Site








Under normal operating conditions, the power system of an electric vehicle is an independent system that is completely insulated from the vehicle casing. However, it cannot be ruled out that the insulation may decrease due to the aging or moisture of the high-voltage wiring harness after long-term operation of the vehicle, which may cause the vehicle body to become electrified. The complex working conditions of vehicles, changes in vibration, temperature and humidity, as well as corrosion from acidic and alkaline gases, can all cause damage to the insulation layer on electric vehicles, resulting in a decrease in insulation performance and the risk of electrical leakage. Therefore, real-time detection of the insulation performance of vehicles is of great significance for ensuring personal safety and safe operation of vehicles.
The insulation resistance requirements we have been discussing, whether at the vehicle level or the high-voltage component level, refer to the resistance between the high-voltage positive/negative and the vehicle body or electrical platform, respectively, and do not include the resistance between the high-voltage positive and negative. There is no true resistance between high voltage positive/negative and the vehicle body, but rather a measure of our insulation design. The insulation design between high voltage positive/negative and the vehicle body is based on basic insulation and grounding, with basic insulation mainly reflected in the design of electrical clearances.
Insulation resistance is used to verify the insulation performance under normal working conditions, corresponding to the insulation performance under extreme conditions, and requires the use of power frequency withstand voltage and impulse withstand voltage tests to verify. In theoretical reality, the high voltage+and high voltage - of the battery pack should have an insulation resistance of ∞ for the entire battery pack casing or vehicle body ground. So in high-voltage battery packs, insulation testing is an indispensable part. The following figure shows the connection circuit between the high-voltage ± of the battery pack and the shell ground. Based on this circuit, the relative resistance Riso+and Riso - can be calculated. As long as one of the resistance values is large enough, the body ground and the battery do not form a conductive circuit, then they are insulated from each other.
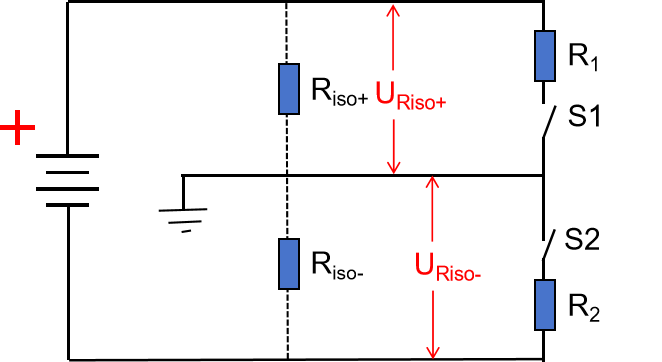
In this circuit, the insulation status of the system is determined by detecting the two ground voltages, URiso+and URiso -. Assuming the system is normally insulated, the resistance values of URiso+and URiso - are very high, and at this point, URiso+and URiso - are close to U0/2. When the insulation against ground decreases, the resistance of Riso+decreases. According to the principle of series voltage division, URiso+will decrease and URiso - will increase. By detecting the changes in these two voltages, it is possible to determine whether there is an insulation problem and its approximate location. Note: When there is an unexpected risk, the relative resistance drops to a certain value, and the high-voltage battery circuit forms a leakage circuit to the vehicle body ground, which will cause a short circuit.